More Air Quality Investigations Coming Up!
Great work! Let’s get on to the next PDQ! Ready. Set. Go!
PDQ1 |
Get ready to offgas some VOCs and hunt up some wild ones!
Grades:
Time:
Subject:
5-8
5-15 minutes
Environmental Science
Volatile Organic Compounds are harmful to your body if you’re exposed to constant, high levels. Let’s take a closer look.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are substances that evaporate at room temperature and are potentially dangerous if we are exposed too heavily. Symptoms of overexposure include headaches, nausea, irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat, loss of coordination and more – yikes!
Sources of VOCs include cleaning solutions, paints, new carpet and furniture, and many other things. If you note a “chemical” smell on something, it is quite likely emitting VOCs.
VOC levels you discover may be quite low, but if you receive prolonged exposure, even of a low level, it can cause harm. Use these values as a general guide:

Let’s explore VOCs further with databot™!
By completing this experiment and conducting the scientific observations associated with it you will master the following knowledge! Good luck science explorer!
Air Quality: The levels of pollutants in your surrounding air determines your air quality. High levels of pollution, dust, or smoke would be examples of poor air quality.
Baking Soda: Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) is an alkaline salt, a base, that can absorb VOCs.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): A colorless, odorless gas naturally present in the air you breathe and is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis. There would be no animal life or green plants without carbon dioxide. Green plants use energy from the sun plus carbon dioxide and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen.
Relative Humidity: Humidity refers to the amount of moisture in the air. High levels of humidity indoors can contribute to microbial activity which can affect indoor air quality.
HVAC: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) refers to the technology of maintaining clean and comfortable environmental conditions in buildings and vehicles.
Indoor Air Quality: The quality of the air inside and nearby buildings that includes humidity and gas levels.
Outgassing: Giving off or releasing gases such as from paint drying and curing.
Vinegar: A mixture of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and water (H20) that gives off VOCs.
Volatile Organic Compounds: Chemicals that evaporate at room temperature and are emitted by substances like cleaners, paint thinner, and paints. Levels that are too high can be harmful to your body and cause health problems.
Volume: The amount of space a substance takes up.
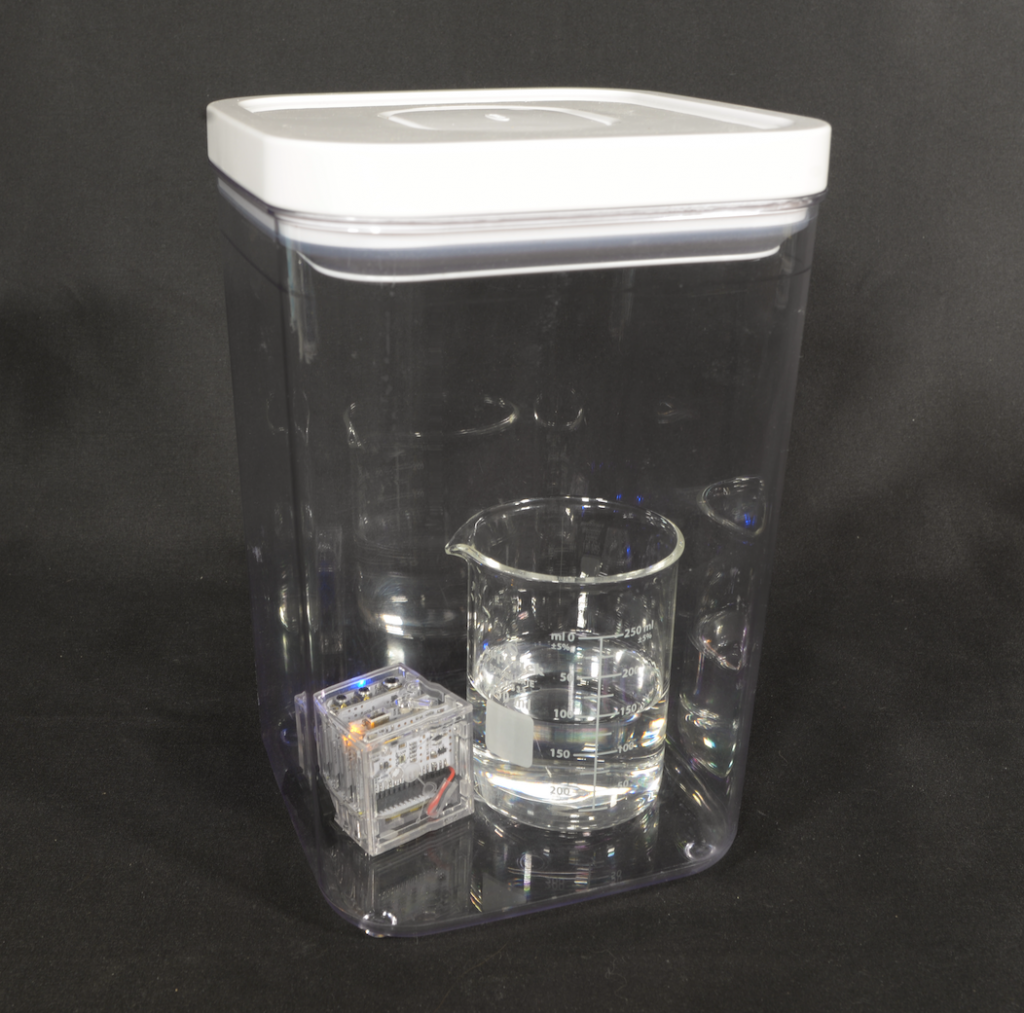

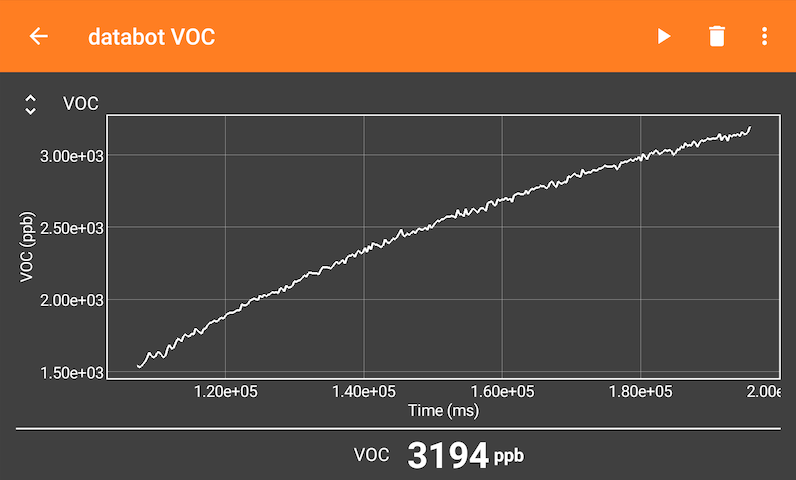
Deep Thoughts with databot™
The Hunt for Wild VOCs
Now that you know about volatile organic compounds and their potential threat to your health let’s check out your classroom or home for possible dangers!
Identify 10 likely places that might be outgassing VOCs. Some places to check:
Use the following chart to note your findings. Good hunting!

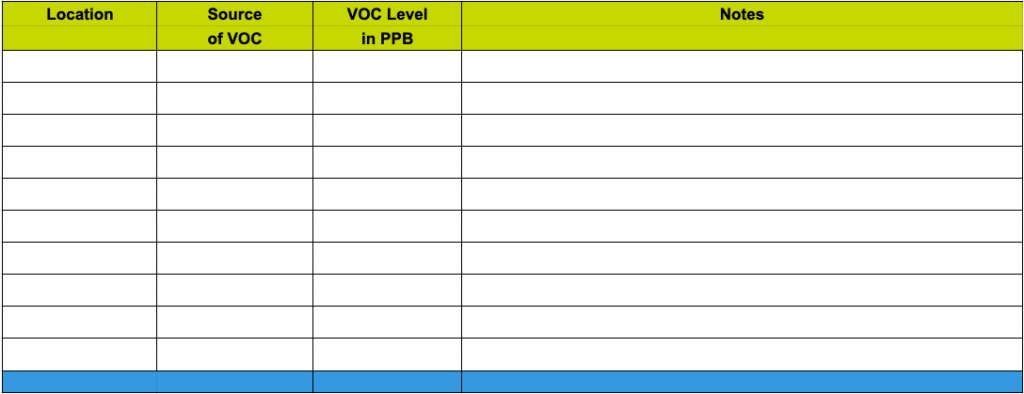
Keep your finished chart handy, you’ll be needing it for the next PDQ!
Great work! Let’s get on to the next PDQ! Ready. Set. Go!
Educator Info
Understand:
Acetic Acid Molecule Image by OpenClipart-Vectors from Pixabay
VOC Spray Bottle Photo by JESHOOTS.COM on Unsplash
Binocular Hunting Image by Free-Photos from Pixabay
 Something in the Air by Robert O. Grover & Team databot™ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at databot.us.com/contact.
Something in the Air by Robert O. Grover & Team databot™ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at databot.us.com/contact.